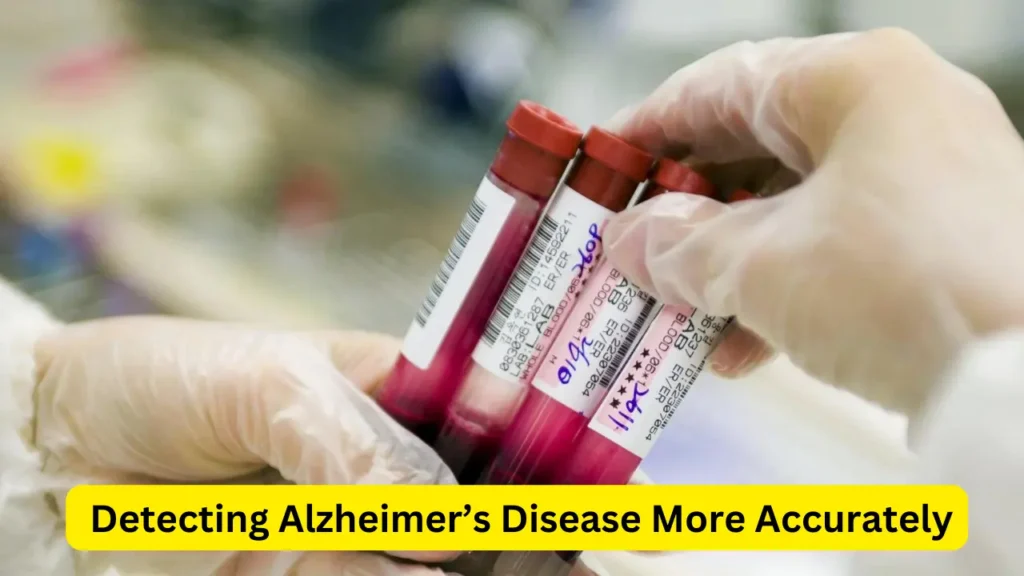
Alzheimer’s disease is a growing concern worldwide, affecting millions of people. Detecting this disease early is crucial for better management and care. Recent research has shown that new blood tests could detect Alzheimer’s disease more accurately than before. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize how we diagnose and treat this debilitating condition.
- Also Read :
- Behind the New Alzheimer’s Blood Test
- Erica Ash, MADtv Star, Dead at 46
- New Blood Tests for Detecting Alzheimer’s Disease More Accurately
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a type of dementia that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases. The disease is characterized by the buildup of abnormal proteins in the brain, known as amyloid plaques and tau tangles. These proteins disrupt the normal function of brain cells, leading to their death.
Current Methods of Diagnosis
Traditionally, diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease has been a complex process. It involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, neurological tests, and brain imaging. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Cognitive Tests: These tests assess memory, problem-solving skills, and other cognitive abilities.
- Brain Imaging: Techniques like MRI and CT scans are used to look for changes in brain structure.
- CSF Analysis: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is analyzed for the presence of amyloid and tau proteins.
Limitations of Current Diagnostic Methods
While these methods are effective, they have limitations. Cognitive tests can be influenced by various factors such as age, education, and language. Brain imaging is expensive and not always accessible. CSF analysis requires a lumbar puncture, which is invasive and uncomfortable for patients.
The Promise of Blood Tests
Recent research has focused on developing blood tests to detect Alzheimer’s disease. These tests aim to identify the same abnormal proteins found in the brain, but in the blood. Blood tests offer several advantages:
- Non-Invasive: Unlike lumbar punctures, blood tests are simple and non-invasive.
- Cost-Effective: Blood tests are generally cheaper than brain imaging and CSF analysis.
- Accessible: Blood tests can be easily performed in primary care settings.
How Blood Tests Work
The new blood tests detect specific biomarkers associated with Alzheimer’s disease. These biomarkers include:
- Amyloid Beta: A protein that forms plaques in the brain.
- Tau: A protein that forms tangles inside brain cells.
- Neurofilament Light Chain (NfL): A marker of nerve cell damage.
By measuring the levels of these biomarkers in the blood, doctors can identify individuals at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Accuracy of Blood Tests
Research has shown that these blood tests have an accuracy rate of about 90%. This is a significant improvement over current diagnostic methods. The tests can detect the disease years before symptoms appear, allowing for earlier intervention.
FDA Approval and Trust
Some of these blood tests have been approved by the FDA, which is a positive step towards their widespread use. However, it is essential to use these tests under the guidance of a healthcare professional. While they show great promise, more research is needed to determine their long-term effectiveness.
Who Should Get Tested?
Blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease are not for everyone. They are most useful for individuals who have a family history of the disease or who are showing early signs of cognitive decline. It is essential to consult with a doctor to determine if the test is appropriate for you.
Ethical Considerations
There are ethical concerns surrounding the use of blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease. For example, discovering that you are at risk of developing the disease can cause anxiety and stress. It is important to provide proper counseling and support to individuals who undergo testing.
Potential Impact on Treatment
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease can significantly impact treatment options. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, but early intervention can slow the progression of the disease. Potential treatments include:
- Medications: Drugs that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, and mental stimulation can help maintain cognitive function.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in research studies for new treatments.
Conclusion
The development of blood tests for detecting Alzheimer’s disease is a significant breakthrough in the field of medical science. These tests offer a non-invasive, cost-effective, and accessible way to diagnose the disease early. While more research is needed, the potential benefits of these tests are enormous. They could lead to earlier intervention, better management, and improved quality of life for millions of people affected by Alzheimer’s disease.